Ford F250 and F350 Diesel: Why Won't My Truck Start?
Diesels have different components that could go wrong and cause them not to start, when compared to a gas engine. Read on to learn how to diagnose your oil burning F250 or F350.
This article applies to the Ford F250 and F350 diesel engine (1994-2003).
Trying to start your Ford truck and getting nothing can ruin your whole day, and make work on the job site grind to a halt. There are various parts that could be responsible for a diesel truck not starting, from electrical components to fuel issues, but most non-starting issues can be fixed without a professional mechanic. The diagnosis is the hardest part, and this guide below will assist you in tracking down the culprit, so read on to learn how you can diagnose and fix the problem with your Power Stroke diesel motor.

Materials Needed
- Socket
- Wrench
- Multimeter
When a car or truck won't start, the first determination you need to make is this: is the motor cranking over and not starting, or does it not even crank when you turn the key? If turning the key cranks the motor, skip down to Step 4 below, otherwise read on and we'll get that motor cranking.
Step 1 – Check the batteries and connections
It could be drained or dead.
Diesel trucks rely on a very high compression ratio to ignite the fuel, instead of spark plugs, so between the size of the pistons and the high compression, they need a lot of juice to crank them up. That is why when you pop the hood you'll find a full sized 12 volt battery on both sides of the motor. The battery is the most common reason why your truck isn't starting.
- Disconnect the negative (black) terminal on both batteries (otherwise you can't test them individually).
- Test the voltage on each with your multimeter set to DC volts.
- Each battery should read over 12 volts.
- If one reads low, replace it.
- If both check out, one or both may still be bad and not able to deliver the proper power under a load.
- Most auto parts stores can test a battery under load for free.
- Clean the terminals and reconnect the batteries.
- Examine the cables for signs of internal corrosion.
- Check the ground connection from the battery cable to the chassis.
- Check the positive battery cable connection to the solenoid, and starter.
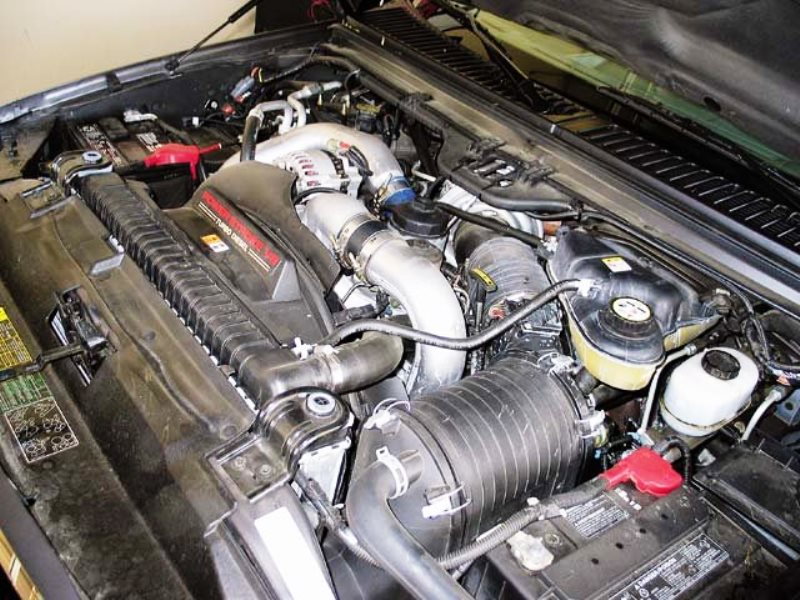

Figure 1. Ford F250 is equipped with two batteries. 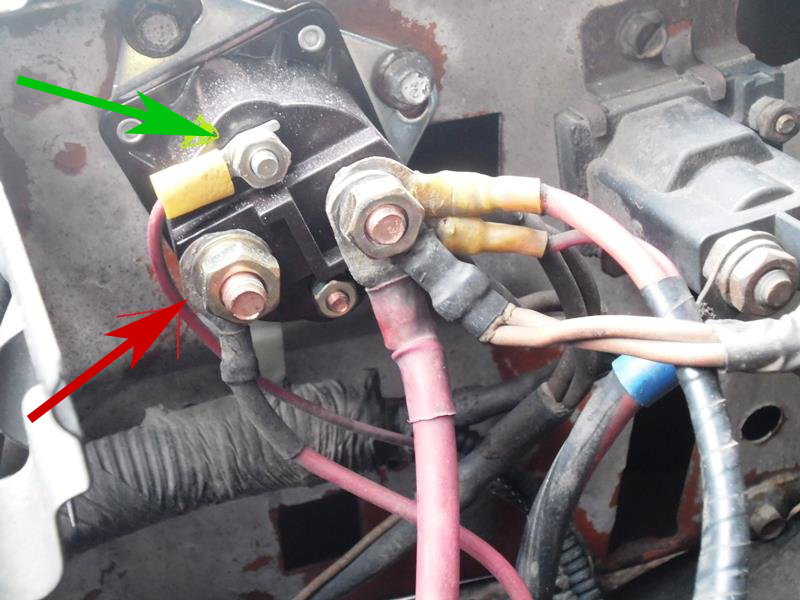
Figure 2. The red arrow is the connection to the battery. The green arrow is the connection to the ignition switch. 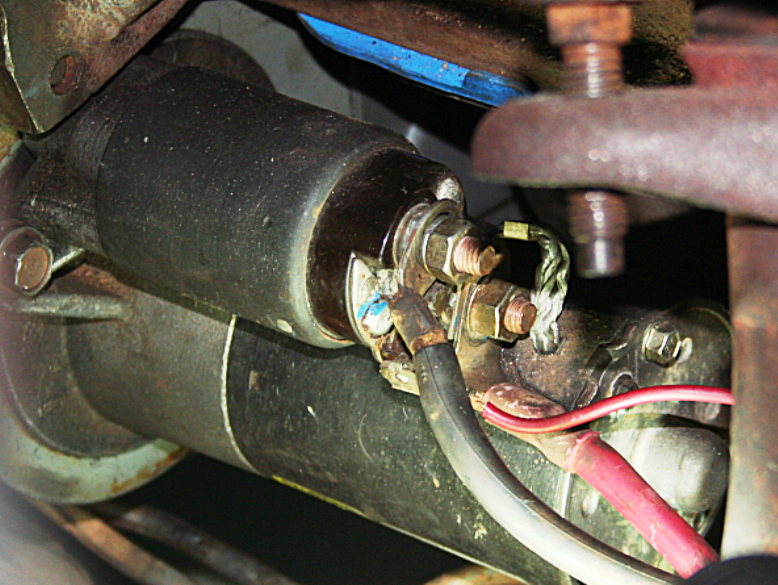
Figure 3. The diesel motor starter has a very tough job.
If the two batteries are working and hooked up properly, proceed to Step 2.
Step 2 – Check the starter and solenoid
You could have a bad starter or relay.
The starter is responsible for cranking your engine to start it—often as it goes bad it needs more and more power to turn the motor over—so when you turn the key, all you'll get is a click or nothing. This shows that your battery is operating properly, but your starter isn't cranking the engine over. The solenoid is an electrical switch which sends the full amperage from both batteries to the starter, without the need for a huge switch inside the truck where the key is. When you do get that click and no start, that is the sound of the solenoid.
- With the multimeter test the voltage at the battery terminal on the solenoid, it should be at least 12 volts, because the batteries are wired in parallel for more amps.
- Hook the multimeter to the small ignition switch terminal on the solenoid and have an assistant turn the key, you should get 12 volts.
- Hook the multimeter to the starter terminal on the solenoid and turn the key again, you should get 12 volts.
- On many of these trucks you don't need to jack it up to reach the starter, so you can perform the same test by connecting to the starter itself and checking for 12 volts when the key is turned.
- If you don't get 12 volts at any of these places when the key is turned, you may have a bad ignition switch, neutral safety switch (in an automatic), clutch switch (in manual), or solenoid itself.
- Also, check for bad connections, pinched or broken wires, or loose terminals.
- If the starter is getting power but still not cranking, you may want to pull it and bench test it or get it tested at your local auto parts store.
If the starter has power and bench tests good, proceed to Step 4.
Step 3 – Check the motor
It could be locked up.
This is rare, but it is possible for the motor itself to get locked up, either because of mechanical issues or "hydro-locked" by too much fuel pooling in the cylinders. If you have a manual transmission, try putting the truck in 1st gear, or reverse, and rocking it back and forth to turn the motor. If you have an automatic, you'll have to use a socket and ratchet on the harmonic balancer bolt. If the problem is hydro-lock, you can take out the glow plugs and try to crank it, thereby pumping out the cylinders. If that doesn't work, say a prayer and check your bank balance, because you likely some serious engine work.

If the motor cranks but the truck won't start, go to Step 4.
Step 4 – Check the glow plugs
They could not be functioning.
The diesel engine doesn't have spark plugs like most trucks, instead, it used glow plugs, which are designed to heat up and assist in starting the diesel engine. Although the glow plugs aren't always essential for starting, they assist the process especially when the ambient temperature is very low. It's recommended you replace the glow plugs when they go bad, which usually is about a year, because the system only works when all of them function properly. If you haven't replaced them for a very long time, then you may have a set of bad glow plugs and will have issues starting the truck.
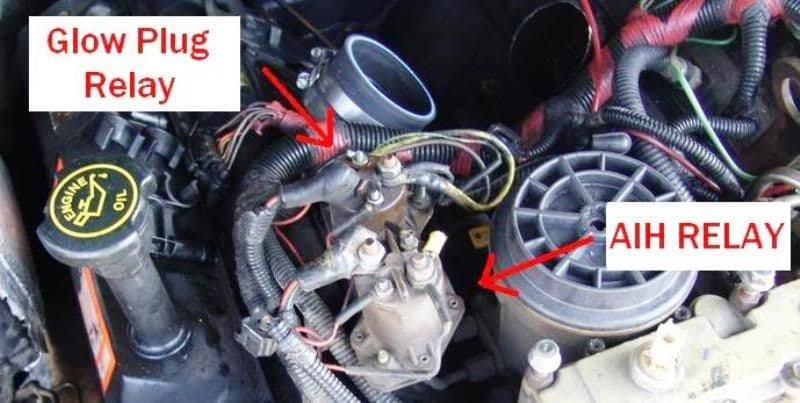

If the glow plugs work, proceed to Step 5.
Step 5 – Check fuel filters
They could be dirty, clogged, or have water in them.
The Ford F250 diesel engine is equipped with two fuel filters, which are designed to filter all the fuel going into the engine, and separate any water out of the fuel. The first fuel filter is located on the driver side's frame rail, right under the driver's door. The second fuel filter is located on the engine, and incorporates the water separater. Remove both filters and inspect them. The fuel filter on the bottom can be checked by blowing on the back of it, and if the air goes through, then it's working properly, but if you feel restrictions, then so does the fuel trying to get to your engine. The second filter in under the plastic cover labeled "Power Stroke," then under a screw off cap. Replace the fuel filters to allow the fuel to flow easier to your engine.
At the bottom of the engine fuel filter housing is a plastic valve, and a metal drain tube. Turn the valve and let the fluid drain. If it is dark and oily, then it is diesel fuel, but if it is clear or cloudy, let it drain into a container until all the water has come out. Put it all back together and try staring the truck again.
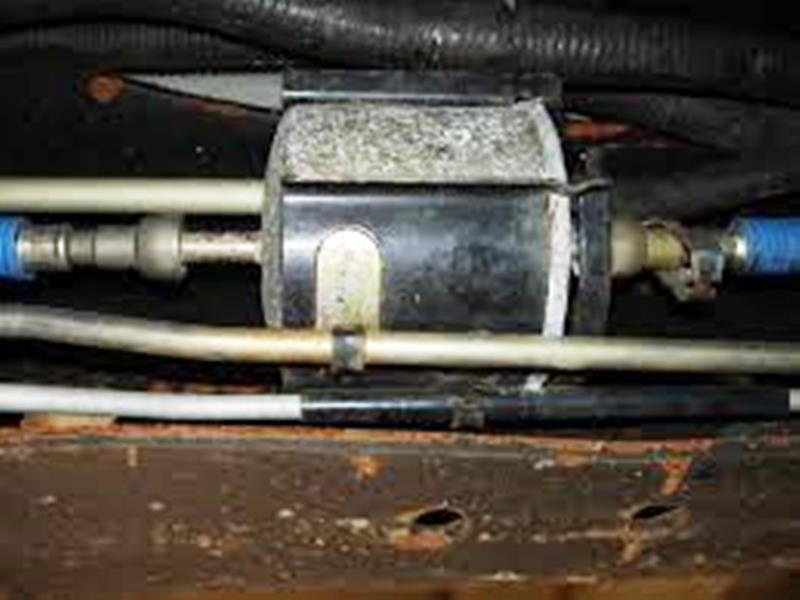

Figure 6. Fuel filter by tank.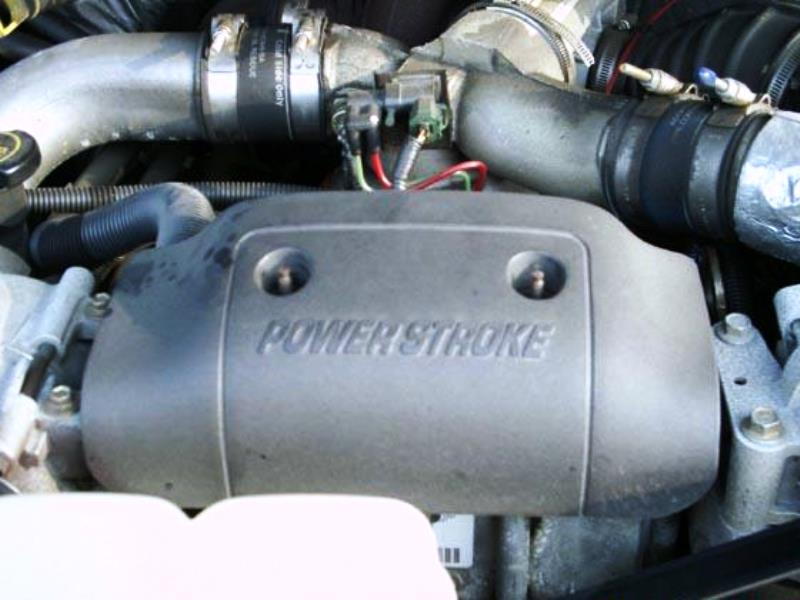 
Figure 7. Power Stroke filter cover.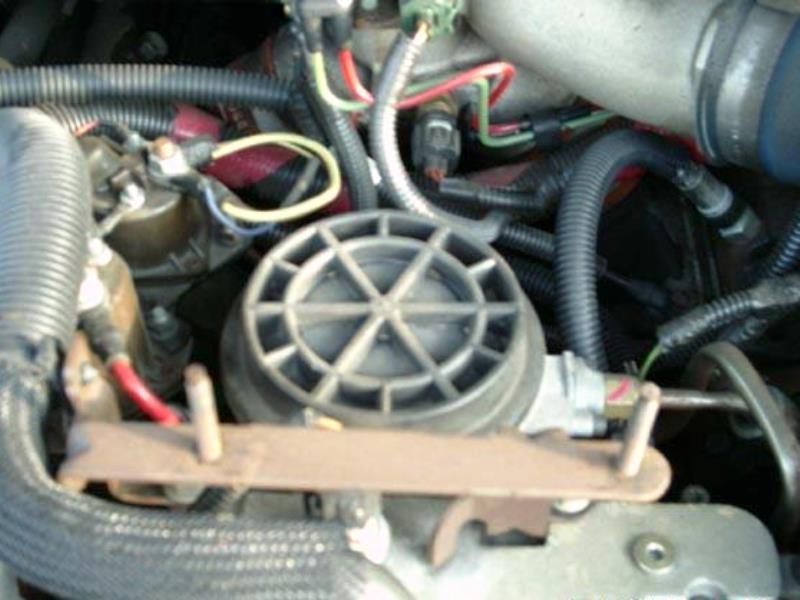 
Figure 8. Fuel filter is under this round, screw off cap, and drain valve is located on the side of it.
Related Discussions
- Cranks but Won't Start - Ford-Trucks.com
- Truck Won't Start - Ford-Trucks.com
- Why Won't My Truck Start? - Ford-Trucks.com






